Human Resource Planning for Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) System Implementation
Info: 10327 words (41 pages) Dissertation
Published: 25th Jan 2022
Research Project on Adequacy of Human Resource Planning and Recruitment processes for the smooth implementation of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system in Field Services, Brisbane City Council.
Executive Summary
The main aim of this research project is to establish the adequacy of Human Recourse Planning and recruitment process for the smooth implementation of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) in Field Services division of Brisbane City Council (BCC). This will give an opportunity to explore the significance of HR planning and recruitment aspects in ERP systems execution and examine their discrepancy in the case of effective and ineffective implementations. This will be beneficial while implementing the ERP systems in other divisions of council in terms of time and cost.
The research purpose of this project is to evaluate the sufficiency of current human resource strategy on Human Recourse Planning and Recruitment process to tackle the main challenges faced during the implementation of ERP system. This will able to establish the key success factors and to convey its importance to the stakeholders for the smooth execution in Field Services of BCC. When referenced, majority of the academic literature advocates that adequate manpower resource is the vital element for any successful implementation of ERP projects. The academic part of this project has intended to attain evidence about the Human Resources and their inferences in ERP implementation process.
A study was steered in the form of a survey and semi structured meetings which were targeted towards different layers of people in the council that has having knowledge on ERP systems and various users who are ultimately the beneficiaries. This research project will be a single case study that mainly aims for the application of Human Resource planning and resource principles. The study will base on the careful analysis of the execution process and a survey through the various users, which focus on quantitative data collection and interviews that accounts for qualitative data collection. The higher management was supportive to the human resource team during the entire planning and implementation period. From the overall perspective, HR strategy was able to convey the benefits of the new system upon implementation to the users. At the same time, it should consider few points raised by the users like recruit external resources, clear direction to the existing users on their career prospects, assurance on job security etc.
This report has 11 sections including references and appendixes as stated in the table of contents. The section 1 is the introduction and gives a brief summary of the purpose, methods adopted for data collection and the outcome of this research project. The section 2 describes about the relevant literature review, case organisation and stipulates the research questions to find the answers. The Section 3 talks about the research methodology and data collection. Analysis of the data and concluding the answers for research questions detailed in section 4. The section 5 stated the implications and recommendations based on research and section 6 is the conclusion of this report. The section 7 listed all the references used and 8 to 11 are the listings of the appendixes framed for this project report.
Table of Contents
Click to expand Table of Contents
1.0 Introduction
2.0 Orientation: Relevant Literature, Case Organisation and Research Questions
2.1 Literature Review: Planning and recruiting aspects of Human Resource
2.2 An Overview on the execution of ERP systems in large organisations
2.2.1 Planning / Critical Success factors for implementation set by HR
2.2.2 Integration
2.2.3 Selection of Employees
2.2.4 Training Employees
2.3 Organisation –Brisbane City Council – Importance of ERP implementation
2.4 Research Questions
3.0 Research Methodology
3.1 Method
3.2 Data Collection
3.2.1 Phase 1 – Collection of data using system observation and on line survey
3.2.2 Phase 2 – Semi Structured group and individual interviews
3.2.3 Ethical Procedures and Consent
4.0 Presentation of findings
4.1 Analysing the data
4.1.1 Analysis of the survey data
4.1.2 Thematic Analysis of the Interview Data
4.2 Answering the Research Questions
5.0 Implications and Recommendations
5.1 Connections to the literature
5.2 Recommendations
6.0 Conclusion
7.0 References
8.0 Appendix 1 – Survey Form
9.0 Appendix 2 – Interview Agenda / Questions
10 Appendix 3 – Organisational Consent – pdf Copy attached
11 Appendix 3 – Personal Consents– pdf Copy attached
Figures and Tables
| No | Details | Page no: |
| Fig 1 | The Manpower activity diagram | 9 |
| Fig 2 | Analysis based on Staff category Vs HR Disciplines | 20 |
| Table 1 | Summary of the survey participants | 18 |
| Table 2 | Overall Survey Feedback from Staff | 19 |
| Table 3 | Thematic Analysis- from Codes to Basic, Organising and Global theme | 23 |
1.0 Introduction
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have come to be a vital tool in the current business processes in recent years. All the main business drivers’ promotes ERP implementation that normally highlights the various strategic benefits, technical, financial and operational benefits these systems offers. As per the statement by Olson et al 2004 that the anticipated benefits of ERP systems comprise earlier information response time, improved interaction across various divisions within the organisation, enhanced administration cycle, less operating and financial expense, better communication with stakeholders, value-added delivery and cash flow system and so forth.
Nevertheless, the above stated benefits are habitually challenging to achieve. Implementing the ERP system is generally a broad and expensive method, which involves considerable amount of work force and other assets, coordinates various interest divisions, handling the cost and time burden together with facing various challenges. In reality, the success rate of ERP implementation is low. Enormous amount of study and research been carried out on issues that influence the implementation procedure to determine the important success aspects that are essential for the rewarding ERP implementation. The outcomes mainly include the importance of human resource aspects like planning and recruitment, appropriate user training, backing from management, stakeholder’s relations, support and collaboration between divisions and finally the communication.
Although various research study and literatures (Hawa et al 2002; Clardy et. al. 2013; Holland et. al. 1999) have recorded that the trained work force features as the main success factor and established that dealing human resources in the right means bring success to the ERP implementation ventures. While adopting the same principles in a local government environment, there are some gaps in translating the previous research principles and study outcomes. This is mainly because of the fact that people are less interested to change from an already used system, feel of incompetence factor in learning and mastering a new system and fear on job security. These labour challenges usually consider managing tougher than any other technological contests. As such, most of the studies points out that many ERP implementation projects fails due to the fact that the organisation pay minimum attention to the human resource aspects.
The inputs and opinions from the users were vital in this case study and direct survey data been collected from various levels of people affected by the ERP implementation. (Saunders et. al 2012) Users from manger to the supervisor level both technical and non-technical disciplines invited to participate in surveys, in-depth semi structured and individual interviews for data collection. The results been analysed thematic coding method, followed by similar group categories.
2.0 Orientation: Relevant Literature, Case Organisation and Research Questions
In this segment, an overview of the related literature on the aspects of human resource planning and recruitment is stipulate in section 2.1. An overview of the context for this research project, which is the execution of ERP systems in a large organisation has described in section 2.2. Especially, in an organisation like city council a local government environment describes in section 2.3. Finally the questions for this research project been described in section 2.4
2.1 Literature Review: Planning and recruiting aspects of Human Resource
The growth of ERP process performance depends on the attainment of the executed re-engineering and integration projects. Mainly, this process is complex in nature and having human resources in suitable means is vital for the success in process implementation (Hawa et al 2002). Most researchers (Welti et. al. 1999; Holland et. al. 1999) have highlighted work force concerns as their major critical success factors during the implementation of ERP projects. The work force activity concerns and difficulties that organisations come across should observe from various angles of the key staff, external experts, internal experts, vendors, system professionals, various stakeholders and users involved in similar projects. This research project analyse the elementary human resource requirements for the fruitful project implementation concentrating on details, outlines and duties of the implementing crew and constant improvement. Aiming on the human abilities will have a through impact on the result of the implementation process (Clardy et. al. 2013). This will ultimately examine the current scenario and improvements in terms of Human Recourse planning and recruitment process in Filed Services for the implementation of ERP/SAP system, which are:
a) Examine the current strategies and shortfalls of human resources planning process and look forward by forecasting the future necessities and quality of resources required to obtain the expected goals.
b) From the planning process and forecast, outline the process of recruiting the potential candidates and encouraging applying for the current or future vacancy. The candidates either within or outside the organisation shall make aware of the requirement, qualification and the career opportunity available to the candidate
Most of the researchers stress that ERP implementation process need the coordination, knowledge and joint recognition from team members of various divisions, which comprise management, consultants, end-users and various stakeholders. This underlines that the human factor will be a key topic in ERP implementation projects. It is recognize that there are three categories of people mainly involved in ERP projects (Hawa et al. 2002)
- Management also termed, as Promoters are the crafters who make the proposal for organising resources and future improvements.
- Internal users or Inhabitants are the people who dictate their need and suggest the areas for improvements.
- Technical staff or external consultants / developers were termed as architects who have the skills required for execution of the needs and improvements stipulated by the promotors or inhabitants.
In a local government environment, any of the above combinations will not achieve the complete expectations of the ERP projects. The involvement of the external agencies/consultant produces a dependency and once they left upon the implementation process, it would be hard maintain or update the system. The relation of the above aspects had shown diagrammatically in the Fig 1 below.
If the organisation depends mainly on in-house trained staff having technical knowledge carries restricted outcomes as they may have a thorough knowledge about their field but might have only limited awareness on the development or improvement of ERP process. Researchers suggest that for a sustainable implementation and improvement process of ERP depends mainly on two human competences:
- Engineering Knowledge which deals with planning and development of the ERP process
- Operation knowledge requires dealing with any issues and transferring the process knowledge to every user for them to make it comfortable and user friendly.
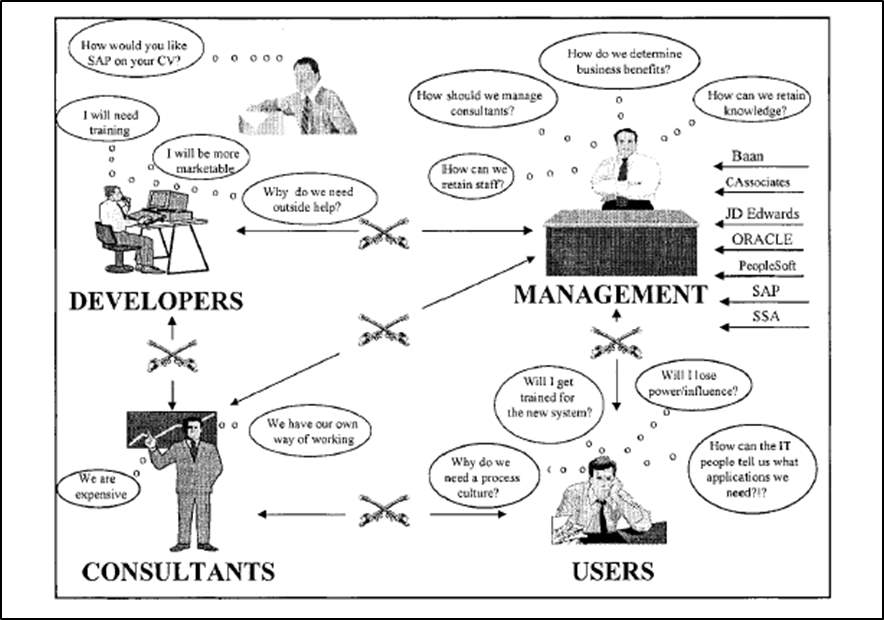
Figure 1: The Manpower activity diagram (Source: Skok et. al 2002)
When a person has both the above types of knowledge is the ideal situation and that helps to run the implementation procedure smoothly between the process and technical environments, which is difficult to achieve. Therefore, most the studies concluded that the aspects of Human Resource like Planning and recruitment is a key factor in ERP implementation for transferring the knowledge and inject confidence to the end users for their daily use. (Gareth et.al. 2007) This would emphasise that not only the implementation team has the understanding of the system usage but also should have the qualities like human competences and abilities.
Welti et al 1999 describes that the main Human Resource abilities required for the successful implementation of any ERP projects are:
- Availability: It is vital to have adequate skilled staff available for the project implementation
- Expertise: If there is deficiency for in house expertise, organisation can recruit new people or else can delegate the capacity to consultants. Getting new people will bring fresh ideas and valuable inputs to the organisation. Even though it is an expensive option, it could fast track the implementation process because of their experience. The negative side is that they may not transfer the knowledge to the users fully.
- Quality: The quality of the implementation crew is the main succuss factor and therefore HR team should give utmost care while selecting the project team. The team should be highly skilled, having the right qualification and being capable of learning new things quickly due to the complexity of ERP projects. The team leaders should have efficient leadership and communication skills together with a long vision about the project implementation. (Stewart et al, 2000)
- Configuration of teams: The configuration of the team shall include skilful leader, capable team members and expert consultants will always produce a positive output for any project implementation.
2.2 An Overview on the execution of ERP systems in large organisations
In recent years, ERP system is becoming an essential tool for the business and services industries. By using ERP system in any organization, it can integrate and co-ordinate various divisions / units. This system will help to flow the information between various sections of the organisation and there by produce better outputs. Although this arrangement brings numerous benefits of the organisation, it can also fetch various difficulties, if it is not execute properly. Appropriate execution required proper planning and their accomplishment. As the ERP system is complex, it will also effect on the corporate operational process. Substantial upper management obligation is vital for the proper application, as its execution includes considerable alteration to the current business practices along with enormous fund investment is required.
Sourcing and handling the suitable consultants is also another task for the organisation, where there is a shortage of able consultants in the market. Respectable ERP vendors will help to ease the cost and duration of execution, through precise resolution and innovative procedure. Getting the skilled and honest employees is another challenge and followed by continues training is to upkeep the knowledge level. (McNamara, et.al. 2008)
2.2.1 Planning / Critical Success factors for implementation set by HR
For the successful implantation of ERP projects, planning is first step by any HR division to consider. Future of the implementation is mainly depends on identifying the critical success factors (CSR) in the planning stage and addressing it systematically throughout implantation and execution stage. (Holland et. al. 1999) The main CSR to consider are:
- Establish a justifiable vision, mission and values
- Building an aligned leadership
- Establishing an suitable organisation structure and procedures to drive the set agenda
- Establish key HR capabilities and systems to implement the processes smoothly
- Appeal, recruit and retain the right set of crew and drive them towards to achievement of the goal.
- Develop the capability to acquire and share best practices
2.2.2 Integration
Organization requires categorizing the details of integration and the way it deals with the whole business operation. As a first step prior to the integration of the system, functional division should analyse the entire system integration and try to fix any errors or mismatches with the procedures that propose by other divisions.
2.2.3 Selection of Employees
The organisations required for a successful implementation of ERP system needs to assign some of their top employees for the job. Few organisations allocate this mission to their in house employees and some other organisation outsources employee’s execution and monitoring the implementation. The overall trend is that internal employees are more enthusiastic when compare to the external people. An internal employee usually puts more effort for the success of the organization. Mostly administrations provide comprehensive recommendation for selecting internal crew for the project. Organisations should go through all the required aspects seriously and select the right candidates for the project implementation.
2.2.4 Training Employees
Continuous training and updating the new techniques of the employees on ERP is a significant challenge. (McNamara, et.al. 2008) Expenditure associated with work force is the most hidden cost for any ERP implementation project. ERP system is lot composite as compared to other system application and therefore it demands suitable training. The frontline users will not be able to handle the requirements of the new system without proper training and the efficiency will drop in a considerable proportion.
2.3 Organisation –Brisbane City Council – Importance of ERP implementation
Brisbane City Council (BCC) is the largest local government department in Australia with 26 wards and 27 councillors. BCC targets to offer the maximum level of consumer satisfaction while maintaining pace with continual change in a highly competitive situation. BCC wanted to instrument electronic communication between departments and divisions to make the council an effective and united department. Council is viewing to marry their finance and stakeholder facility processes; they were considering also relating the crew in the field with all resources they need to get the job done. The amount of spell required to visit a site, gauge the situation and plan resources before outlining a strategy was waste of time, according to the council. Further, considering an arrangement that would facilitate to close the gap and take time to resolve the problem at the soonest possible. In order to be a united council, the management team recognized that they have to assess various Enterprise Planning (ERP) systems. The Human Resource (HR) linked with the Strategic Management of Council to establish and implement the vision and mission of achieving the one council policy through the Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM)
The customary Human Resource Management measured as one directional, inflexible and strained but Strategic Human Resource Management emphases on flexible, extensive and cooperation arrangement of job design. (Ostreman et. al. 2010) The most important role in current HR strategy is to recognize the staff as the significant assets of the organization and invest to improve their abilities and knowledge. (Noe et.al. 2015)
Human Resource plan carries a flawless direction for the organization to foresee the future and opportunity in terms of its Human Resources. A long-term strategic plan permits the council to distinguish the opportunity, and threats, assess internal strengths and weaknesses (SWOT Analysis), and determine viable advantage. (Noe et.al. 2015) The implementation of the SAP systems for the council was a huge challenge to the HR because of the resistance from various employees due to several factors. Numerous age groups, academic backgrounds, hesitancy to accept the fresh systems and to omit the familiarised methods are the various key factors recognized by the HR team. The constant development and to attain strategic management goals fixed by the management, HR strategy comprises the expansion of various mechanisms of the Human Resource Management (Baligh et. al. 2006) and those mechanisms recognized are:
- Organizational Structure
- Job Analysis and Evaluation
- Recruitment and its Selection Process
- Training and Development
- Performance management and Appraisal
- Reward and Employee Benefits
2.4 Research Questions
The main aim of this research project is to assess the adequacy of existing human resource strategy on Human Recourse Planning and Recruitment process to configure the main obstacles faced during the implementation of ERP/SAP system. This would establish the key susses factors and to express its prominence to the stakeholders for the smooth execution of ERP in BCC. The main critical success factors for the organisation that affect the success of ERP/SAP implementation, which would reflect and scrutinised are forming clear objectives, setting scope, establishing goals and recruitment process.
The research project will also focus some of the key concerns that may effect during the implementation of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP). These issues include indistinct goals, missions and vision, deficiency of resources to attain end user teaching, unsuited organization culture and insufficient administration of knowledge (Noe et.al. 2015).
The questions can classify in three sections:
- How the current HR strategy for the implementation of ERP in terms of resources planning meets the requirement of the goal setting and demand forecast. How to improve if there are any shortfalls identified?
- How the current resource strength meets the demand for the ERP implementation process and what are the changes to propose?
- How the new HR planning and recruitment process convey the stakeholders on the benefit while implementing the ERP system in the other divisions of the council?
3.0 Research Methodology
This section describes the research methodology adopted in this research project. This research project will be a single case study that aims for the presentation of HR planning and resource principles for the effective execution of ERP in Field Services of Brisbane City Council. This would emphasis on the methods implemented to breach the existing challenges and the tactic to embrace the principles of HR planning and recruitment processes for attaining the goal, which is execution of ERP in BCC. (Robert et. .al. 2014) The research will base on the vigilant analysis of the implementation method and a survey among the several users, which aim on quantitative data collection and interviews that relates for qualitative data collection (Saunders et. al. 2012).
3.1 Method
A single case study research has chosen as the methodology to answer the research questions. This shall justify the opportunity to explore the impact of planning and recruitment aspects of HR in the organisation to address critical concern of how to execute smoothly the implementation of ERP (Robert et al 2014). This research approach used to create a deep, multi-faceted understanding of a compound issue in its real-life context. In addition, it is a conventional research design that use broadly in a wide variety of disciplines, mainly in the area of Human Recourse. Case study research approach could be either a qualitative or a quantitative approach. In the qualitative approach, this states to in depth analysis of a single or small number of units. A unit selected for a case study can include a single or a group of people, a division or an entire organisation. (Saunders et. al. 2012)
This method is also termed as a good tool to study in detail the existing HR aspects and practises (Saunders et. al. 2012). With the knowledge attained from 9 years of experience in BCC using the BIRT (Old system) and ERP (new system), survey data, semi structured interviews and various literature reviews form the platform to conduct the research and analyse quantitatively and qualitatively its outcomes. The reason for using both the analysis in this research study is to achieve a more conclusive and error free outcome by improving both internal consistency and generalizability through combining both quantitative and qualitative methods in the same study. (Ashatu et al 2008)
3.2 Data Collection
The main approach to attain the requirements on the shortfall of HR planning and recruitment aspects during the ERP execution process adopted was the focused observation on the existing practice and the interactions with the key informants. This has followed with a survey and the semi-structured interviews with the selected handlers keeping in mind to clarify the points observed and to make clarity on the situation. (Saunders et. al. 2012)
Collection of primary data using survey questionnaire has used to attain quantitative data for the analysis. This questionnaire has made in a simple way (Appendix 1), which has given a better response rate with a reliable outcome. A questionnaire has distributed to the participants from managers to the site team leaders through electronic mail and the outcome has analysed through tabulation. The quantitative data from survey questionnaires shall use to form the framework to analyse the effectiveness HR Planning and recruitment process during the implementation and the suggestions for further improvements (Carson et. al. 2001). Qualitative data has collected using semi-structured interviews and the data shall be theme analysed using simple thematic coding method followed by categorisation of the data into smaller groupings in two steps as axial coding and selective coding. (Newman et. al 2014) “The qualitative case study is an approach to research that facilitates exploration of a phenomenon within its context using a variety of data sources”. (Baxter et al 2008)
The survey questionnaires been distributed to 50 selected participants. The participants been classified into three categories as Executive, Administration and Field staff. From 50 selected participants, invited 16 of them in three different sessions for the semi structured interviews.
3.2.1 Phase 1 – Collection of data using system observation and on line survey
As a first step, observation technique been used to find the shortfalls and the merits in the current system used. Observation, predominantly participant observation been used in a range of disciplines in the division as an instrument for gathering data about adequate manpower skills, training, processes, methods and procedures in qualitative research. Because of the ethical considerations, overt type of observation been adopted in this research. Observation approaches are valuable to researchers in many ways. They deliver researchers with means to check for nonverbal expression of emotional state, define interaction between the team members, understands how participants converse with one another, and monitor the time spent on various activities.
The observation technique was very useful to monitor the existing scenario within the division and helped to prepare the questionnaire for the online survey and the subject to discuss for the semi structured interviews.
Further to the focused observation, a survey conducted based on the questionnaire prepared as attached in Appendix 1. The questionnaire been structured with a 4 point scale as Yes /No/Unsure/Other comments. The percentages of respondents who supports the points raised were marked ‘yes’ and opposes marked ‘no’. Small percentage of the participants has taken a neutral stand and marked as ‘unsure’ and some of them add additional comments. The questionnaire been distributed to 50 selected participants which includes managers, engineers, planners, administration officers, senior supervisors and team leaders on site. From the 50 participants only 31 (62%) been returned the questionnaire marking their point of view.
3.2.2 Phase 2 – Semi Structured group and individual interviews
This phase was a detailed study to find the main critical impacts of the HR aspects during the implementation process of ERP. This phase mainly focused on qualitative data. “The qualitative study is often associated with an interpretive philosophy because researchers need to make sense of the subject and socially constructed meeting expressed by those take part in the research about the phenomenon being studied” (Saunders et al 2012).
Data collection consisted of semi-structured interviews with various mix of 16 users (11 office based staff and 5 field base staff) which has given a fair opportunity to extract the issues and details from the users. A judgmental approach has adopted to size the group of interviewers based on the grade and the scope of work they handle in the organisation. Interviews took place over three weeks (5th July to 13th July) in the office for the office based staff (Managers, Engineers and Admin staff) and on field for the site based staff (Supervisors and Team leaders) All the meetings were conducted based on the agenda attached in Appendix 2 and conversations and the feedback been recorded during the interviews. The close of the meeting, the recorded notes been read and agreed the content with all the participants to avoid any ambiguity.
3.2.3 Ethical Procedures and Consent
Permission been granted to do this research project by the Field Services Manager for construction of Brisbane City Council (BCC). As outlined in the ethical guidelines in the AIB learning materials, all the participants were signed the individual research consent form to express their willingness to participate in the survey /interview in relation with this research project. As per the sake of the confidentiality the management and the staff participated in the survey been assured that their names would not be attributed to comments they made in this research report and their participation is voluntary and they could withdraw their signed consent any time they wish. Signed consent forms for both organisational and personal has attached in Appendix 3 and 4 respectively.
4.0 Presentation of findings
4.1 Analysing the data
4.1.1 Analysis of the survey data
Quantitative research mainly explores specific and clearly defined questions that examine the details of the issue connected with the research topic. Quantitative data often collected through surveys, questionnaires that are sensibly established and designed to provide with numerical data that can explored statistically, and yield a result gives specific solutions. (Neuman et. al. 2014)
All together 50 questionnaires has distributed to the selected individuals mainly classified into three categories as Executive, Administration and Field staff who have had considerable contribution with the usage of ERP system in the organisation. From the total distributions, only 31 questionnaires have returned yielding a 62% response rate. The questionnaire prepared to extract the actual feedback from the users on various issues related to the aspects of Human Recourse planning they face during the implementation and maintenance of ERP.
From the table 2 below, it can be summarised as almost 60% of the staff are supporting the current HR strategy. Majority of the staff are supportive with HR governance of the organisation and only 58 % accepts the current HR training, benefits and compensation in place are adequate to support the current ERP implementation process. Further the opinion on the skills, knowledge and the time line it is quite evident that they support for outsourcing technical experts and more duration for the implementation stage.
Below table: 1 shows the profiles of respondents:
| Si No | Disciplines | Number Responded | Percentage | Remarks | Staff Category |
| 1 | Managers | 6 | 12.9% | Management | Executive Staff |
| 2 | Engineers | 2 | 12.9% | Technical | |
| 3 | Planners | 7 | 22.5% | Planning | Administration Staff |
| 4 | Admin Staff | 6 | 22.5% | Accounts & Procurement | |
| 5 | Supervisors | 4 | 12.9% | Site Staff | Field Staff |
| 6 | Team Leaders | 6 | 16.3% | Site Staff |
Table 1: – Summary of the survey participants
The table 2 below shows the overall feedback from the staff based on various aspects of HR issues:
| Si No | Issues Addressed | % – Yes | % – No | % – Unsure | %-Other Comments | HR Disciplines |
| A | Support of current HR Strategy | 62 | 18 | 15 | 5 | HR Strategy |
| B | Annual Planning and Review process | 65 | 17 | 10 | 8 | |
| C | HR Planning on ERP implementation | 50 | 28 | 18 | 4 | |
| D | Equal Employment Opportunity | 80 | 15 | 3 | 2 | HR Governance |
| E | Code of Conducts | 85 | 15 | 0 | 0 | |
| F | Performance Appraisal | 88 | 12 | |||
| G | Training & Staff development | 69 | 13 | 12 | 6 | HR Training / Benefits & Compensation |
| H | Opportunity for professional development | 63 | 25 | 8 | 4 | |
| I | Gauging Non Performance | 50 | 35 | 15 | ||
| J | Adequate benefits & Compensation | 48 | 36 | 5 | 11 | |
| K | Strength & Knowledge of Implementation team | 63 | 29 | 4 | 4 | Strength, Knowledge & Time line of implementation team |
| L | Requirement of Outsourcing skills | 76 | 18 | 1 | 3 | |
| M | Review of current work load of the team | 58 | 26 | 10 | 6 | |
| N | Implementation time line | 61 | 18 | 15 | 6 |
Table 2 – Overall Survey Feedback from Staff
The survey results been analysed further based on the staff category vs HR disciplines and Fig 2 below describes the outcome. From the results, it shows that majority of the executive staff supports the current HR strategy and the methods adopted for the implementation. The Admin staffs are of the opinion that it is adequate but needs improvement and among the field-staff, more that 50% voice out that more effort and time required them to understand and learn the new system effectively. In addition, they need expertise to train the usage, as this is a new system and most of them not computer literate.
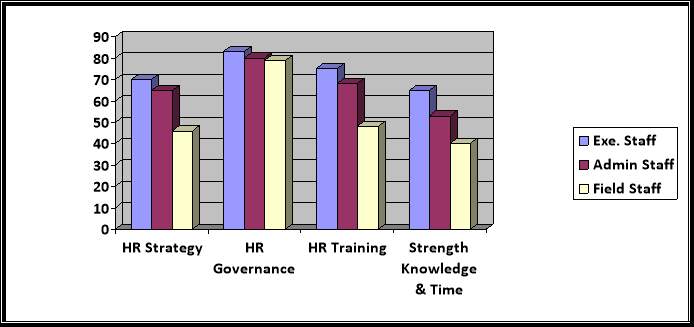
Figure 2: – Analysis based on Staff category Vs HR Disciplines
4.1.2 Thematic Analysis of the Interview Data
Qualitative data analysis is a procedure that pursues to ease and make sense of enormous amounts of information often from various sources so that the expressions will shed light on a research question can occur. Qualitative data analysis naturally turns around the expressions and interpretations of key researchers. Qualitative data analysis should pay consideration to the spoken word situation, reliability and inconsistencies of views, frequency and strength of comments, their specificity as well as emerging themes and trends.
In this research project for the quantitative analysis, semi structured interviews were conducted at three occasions with various staff categories. The first meeting conducted on 5th July 2017 with five executive staff (3 managers and 2 engineers) which took 35 minutes. Second meeting held on 7th July 2017 for about 45 minutes with administration staff and this group has six participants includes three planners and three accounts & procurement staff. Finally, the third meeting conducted on site for 40 minutes with five field staff (2 supervisors and 3 team leaders) on 12th July 2017. All the meetings were conducted based on the agenda attached in Appendix 2 and conversations and the feedback been recorded during the interviews.
The general outcome of the interview based on three different staff categories are as stated below,
Executive Staff: They have a high rating on the information quality and the job design set by the current human resource strategy. They prefer to get some additional external resources to bring in new methods and techniques, which would enhance the knowledge transfer. Most of them supports the implementation of the new ERP system and happy with the current situation on rewards and job security. Their point of view is that if HR could recruit new qualified resources, frequency of group training can reduce.
Administration and Field Staff: Comparatively they have rated low on the HR strategy in terms of information quality and job design. Majority of them have the same opinion as executive staff on recruiting qualified external resources to enhance the method of knowledge transfer. They have expressed their concerns on compensation, rewards and job security. Most of them are not fully convinced of the advantages and benefits achieved through the implementation of new ERP system.
From the outcome of the above meetings, the data was analysed thematically using a simple thematic coding method followed by categorisation of the data into smaller groupings. It noticed that not all the codes listed are relevant to the research topic and therefore chose the right cluster of codes into basic theme. Further, examine the basic theme and cluster them together into higher order and more intensive organising themes and through this the main research objective can be focused. The diagrammatic representation of the thematic analysis based on the interview data shown in the Table 3 below.
| Codes | Basic Theme | Organising Theme | Global Theme |
| Quality Information | Basic view is that further improvement is required job design & analysis which enhances the quality of information transferred to staff | Recruit and retain relevant resources which help to carry out proper job design and analysis and transfer the knowledge to the existing users | ERP Implementation |
| Proper job Design / Analysis | |||
| Sufficient resources | General view is that external resources required to update the system knowledge which minimise the staff turnover | ||
| Staff Turnover | |||
| Training & Development | Intensity of training and development shall be increased and should allow more time for the staff to get the feel of the new system | Management should take measures to enhance the Training & Development. This will give confidence to the existing users which results a beneficial outcome to the organisation | |
| Monitoring Performance Management | |||
| Compensation Rewards & Job security | Management should take care of the compensation side to the right staff in terms of the workload and give confidence on the job security. Convey effectively the benefits of the new system gathered through stakeholder’s satisfaction survey and annual budget savings. | ||
| Comparison between new & old System |
Table 3: – Thematic Analysis- from Codes to Basic, Organising and Global theme
4.2 Answering the Research Questions
Question 1 – How the current HR strategy for the implementation of ERP in terms of resources planning meets the requirement of the goal setting and demand forecast. How to improve if there are any shortfalls identified?
From the outcome of the survey and interviews, almost 50% of admin and field staff who are the main users of the ERP system points out that the HR strategy should assess the job descriptions occasionally mainly in agreement with a reward study and whenever the organisational system changes. It is the process of examining and construing data about the job’s tasks and accountabilities. This mainly covers pursuing an employee’s commitments and the term of every assignment, sensing the employee achievement of the job, converse with the user, managers and other stakeholders who interacts with the employee. The concluding output of the current strategy that it needs a detailed understanding of the important tasks of the work and a list of all responsibilities and duties of every key resource. With this, the management should able to assess the future forecast of the resource based on the target duration set for the ERP implementation.
Once the above strategy is in place then the following periodic actions should adopt in the organisation for the improvement of the implemented systems:
- Include employees giving them to complete job analysis forms.
- Interview employees, inquiring them detailed questions about their job duties and responsibilities.
- Log sheets from employees with evidence about their jobs and the amount of time consumed on every work.
- Desk audits where you detect employees doing their jobs at various times of the day.
- Conduct one to one Interview with supervisors and managers, and other employees, clients and customers.
Question 2 – How the current resource strength meets the demand for the ERP implementation process and what are the changes to propose?
Human Resource strategy brings a perfect direction for the organization to foresee the future and opportunity in terms of its Human Resources. It is a long-term strategic plan, which permits the organisation to analyse the opportunity, and threats, assess internal strengths and weaknesses (SWOT Analysis), and establish viable benefit. The execution of the ERP systems was a big challenging task to the HR team due to the resistance from the employees due to numerous factors. Various age groups, educational qualifications, unwillingness to adopt the new systems and to leave the already familiarised processes are some of the main factors recognized by the HR team.
From the survey and its quantitative analysis, it is pointing towards the direction that almost 70% the executive team is supportive of the current strategy and the usage of in house resources. In terms of administration and field staff, almost 50% voice out that they prefer to recruit external resources for transferring the knowledge and techniques. This will make them understand the basics and give confidence for the comfortable usage of new ERP system.
The participants propose that HR strategy should involve more with the careful development of various components of the Human Resource Management for the ERP implementation and the components identified are (Enrich et.al. 2009):
- Organizational Structure
- Job Analysis & Job Evaluation
- Recruitment and Selection Process
- Training and Development
- Reward and Employee Benefits
Question 3 – How the new HR planning and recruitment process convey the stakeholders on the benefit while implementing the ERP system in the other divisions of the council?
The HR team plays an important role in guaranteeing and observing that recruitment and selection processes are impartial, moral and effective.
An effective recruitment and selection procedure will:
- Draw skilful individuals for suitable roles
- Furnish a various staff team
- Match people to the job
The HR manager is responsible for ensuring that appropriate procedures fulfilled in the recruitment and selection process.
The Council’s recruitment process shall include the following steps:
- Strategic review of the position
- Provide the package information to the applicant
- Conduct interviews and selection process following the merit and fair principles.
- Referee and back ground checks
- Approval
- Employment offer
- Orientation for the appointed staff
- Completion of all documentation related to the employment process.
Methodical recruitment and selection processes that eradicate biased practices inspire diversity and ensure that poor candidates not given access to job opportunities. This will help the implementation team to execute the required target and goal in the stipulated duration. In order to convey the effectiveness of the successful HR planning and recruitment to various stakeholders, a quantifiable output has to be established. During the semi structured interviews, the following proposals been suggested by majority of the participants:
- Customer satisfaction survey and its analysis upon the implementation of ERP
- Comparison of actual implementation period Vs target duration
- Comparison of annual cost savings of resources with past 3 years
5.0 Implications and Recommendations
5.1 Connections to the literature
Successful implementation of any new systems in an organisation is totally depends on the involvement, dedication and the confidence of the system users. If they approach the methods positively then the transformation of the knowledge become easier for the HR / Management. Any strategy of policy adopted by HR should base on this aspect. A planned HR strategy can lead any organization to mature its human resources to accomplish the overall business strategy (Noe et.al. 2015).
From the above study it is clearly defined that HR strategy should evaluate the job descriptions periodically in line with a reward study, whenever the organisational system changes. HR strategy should able to convey the benefits of the new system upon implementation precisely to the users and it shall give clear direction to the existing users on their career prospects and job security.
5.2 Recommendations
From the overall view of the qualitative and quantitative analysis, human resources strategy has empowered to achieve a great deal of success so far. Perhaps, HR Management should stress on making its strategy more comprehensive and receptive to the developing human resources concerns. (McNamara, et.al. 2008) Precisely, concentrating in the following areas shall benefit the company in building its human resources strategy more effective.
- Payment of higher wages for the technical employees engaged to support the implementation.
- Making the recruitment and selection policy adoptive.
- Training and development shall plan in different levels depend on the calibre and educational background of the user.
- Clear direction to the existing users on their career prospects upon implementation of new ERP system.
6.0 Conclusion
The Implementation of Enterprise Planning system in Field Services of City Council (BCC) was quite complex due to several reasons. The main reason was the approach of the existing users to settle for a change from the used system, which has practised for several years. Another issue was the self-reliance levels of the majority of the admin and field employees to use a comprehensive computer based system and the job security upon the implementation. The higher management was supportive to the human resource team during the entire planning and implementation period. From the overall perspective, HR strategy was able to convey the benefits of the new system upon implementation to the users. At the same time it should consider few concerns raised by the users stipulated above in research answers (4.21, 4.2.2 & 4.2.3) and Implication and recommendation under item 5.0, for the smooth implication of ERP system. Once the users start this process and getting more confidence using the Enterprise and Resource Planning software, all information is readily available and the dealings become more transparent. The mission and goal of BCC to be a ‘One Council’ policy will achieve with the successful implementation of ERP system, within the targeted duration of 12 months.
7.0 References
Ashatu H, 2008, The use of Triangulation in Social Science Research: Can Qualitative and Quantitative methods be combined; Journal of Comparative Social Work
Baligh, Helny H, 2006, Organisation Structures, Theory and Design, Analysis and Prescription, Springer US
Baxter P, Susan J 2008, Qualitative Case Study Methodology: Study Design and Implementation for Novice Researchers, vol. 13 pp 544-559
Carson, D, Gilmore, A, Gronhaug, K & Perry, C 2001, Qualitative Marketing Research, 1st edn, SAGE Publications Ltd London
Clardy A 2013, A General framework for performance management systems: structure design and analysis, performance improvement, vol.52, 20.2, pp5-15
Enrich P, Leonard D, Jeanette G 2009 A practical Guide to Job Analysis, Pfeiffer.
Gareth R, 2007 Recruitment and Selection, 3rd Edn, Jaico Publishing House
Hawa M., Ortiz A., Lario F., Ros L. 2002, Improving the role played by humans in the development of enterprise engineering and integration projects through training based on multimedia. International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, Vol. 15, No. 4, pp. 335-344
Holland, Light and Gibson 1999, A critical success factors model for enterprise resource planning implementation. Proceedings of the 7th European Conference on Information Systems, Copenhagen Business School, Copenhagen pp. 273-287
McNamara, Carter, 2008. Employee Training and Development: Reasons and Benefits. New York, Authenticity Consulting, LLC
Neuman, W.L, 2014 Social Research Methods: Qualitative and Quantitative Approaches, 7th edn, Pearson Education
Noe, R. A., Hollenbeck, J. R. Gerhart, B. & Wright P, 2015, Human Resource Management, 9th Edn, Mc Graw Hill Education
Olson D. L. 2004, Managerial Issues of Enterprise Resource Planning Systems McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Ostreman, P 2010, Job design in the context of the job market, Journal of Organizational behavior, vol.31, no.2/3,pp.401-411
Robert K Y, 2014, Case Study Research Design and Methods, 5th edn, SAGE Publications Ltd, London
Saunders, M, Lewis, P & Thornhill, A 2012, Research methods for business students, 6th edn, Prentice Hall, London
Skok W., Legge M. 2002 Evaluating enterprise resource planning systems using an interpretive approach. Knowledge and Process Management, Vol. 9, No. 2, p.74
Stewart G., Milford M., Jewels T., Hunter T., Hunter B. 2000, Organizational readiness for ERP implementation, In proceedings of the Americas Conference in Information Systems
Welti N. 1999, Successful SAP R/3 implementation: Practical management of ERP projects. Pearson Education Limited
https://www.brisbane.qld.gov.au/about-council/governance-strategy/vision-strategy
8.0 Appendix 1 – Survey Form
Survey on HR Planning and Recruitment process on ERP Implementation
- Do you feel current HR Strategy supports the ERP Implementation process?
| Yes | No | Unsure | Other comments |
- Does the HR section undertake annual planning process and review process?
| Yes | No | Unsure | Other comments |
- Have you been briefed the HR plan on ERP implementation Scheme?
| Yes | No | Unsure | Other comments |
- Have you been briefed the Equal Employment opportunity?
| Yes | No | Unsure | Other comments |
- Have you been briefed the code of conducts?
| Yes | No | Unsure | Other comments |
- Is there an opportunity for the professional development in the organisation?
| Yes | No | Unsure | Other comments |
- Is the training and staff development adequate?
| Yes | No | Unsure | Other comments |
- Is there a regular performance appraisal system in place?
| Yes | No | Unsure | Other comments |
- Is there any system in place to gauge the non-performance issues among the staff?
| Yes | No | Unsure | Other comments |
- Does the approach towards benefits and compensation is adequate?
| Yes | No | Unsure | Other comments |
- Is the current strength and knowledge of the ERP implementation team adequate?
| Yes | No | Unsure | Other comments |
- Do you think outsourcing skills is essential for smooth implementation?
| Yes | No | Unsure | Other comments |
- Do you think the current workload of the staff to review?
| Yes | No | Unsure | Other comments |
- Is the time line set for the implementation being realistic?
| Yes | No | Unsure | Other comments |
- Is there any other suggestion, which benefits the implementation of ERP?
Interview for the feedback on challenges during the implementation of ERP
9.0 Appendix 2 – Interview Agenda / Questions
| Group meeting : Discussion on the challenges during the implementation of ERP in Council | |||
| Meeting Details:
Date: Start Time: Location: Conducted by: Elapsed Time: |
Participant Data: | ||
| Meeting Introduction by the Chair: | |||
| Purpose | A brief description about the meeting | ||
| Confidentiality | Explain / Assurance about the confidentiality of the matters discussed in the meeting | ||
| Questions to Discuss:
especially on:
|
|||
| Wrap up | Thanks to all the participants | ||
10 Appendix 3 – Organisational Consent – pdf Copy attached
A pdf scanned copy separately attached
11 Appendix 3 – Personal Consents– pdf Copy attached
A pdf scanned copies separately attached
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
All TagsContent relating to: "Business Strategy"
Business strategy is a set of guidelines that sets out how a business should operate and how decisions should be made with regards to achieving its goals. A business strategy should help to guide management and employees in their decision making.
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this dissertation and no longer wish to have your work published on the UKDiss.com website then please:




