Impact of E-Commerce on Consumer Buying Behaviour
Info: 8029 words (32 pages) Dissertation
Published: 27th Sep 2021
Tagged: E-commerceConsumer Decisions
A study of the UK supermarket industry
TABLE OF CONTENTS
CHAPTER – 2: Literature Review
2.2. Internet as an Important Communication Tool
2.3.1. Customer Perception and Attitude about E-Commerce
2.3.2. Consumer Attitude towards E-Commerce Tools
2.4.1. E-Marketing Tools and Trends
2.4.1.2. Employing Email Marketing Methods
2.4.1.3. Online Advertisements
2.4.1.5. Electronic Word of Mouth (Viral Marketing)
2.4.1.7. Advertisement fatigue
2.5. Critical Success Factors of E-Marketing Strategy
Chapter 5: Presentation & Discussion
CHAPTER – 1: Introduction
1.1. Introduction
The advancements and developments in computerised hardware and sophisticated software over the past two decades has influenced the way organisations conduct their business in current highly complex and competitive globalised markets. Kotler and Armstrong (2010) are of the view that starting from traditional shops where consumers had to go physically for making purchases, the companies initially started providing a brick and mortar system in which consumers were allowed choice between going to the store, or making purchases online from official websites of the company. Valvi and West (2012) furthered on what Kotler and Armstrong (2010) stated and discussed the increase in online businesses without any physical presence in shape of shops.
It is not only the change in the way businesses conduct their business operations, the change has also occurred in the way consumers search, analyse, compare, and purchase products and services. While traditionally the consumers used to physically go in stores, look at the products, and decide whether to buy it or not, in current marketplace, online websites allow consumers to view, compare, and purchase products from the comfort of their own home. A general perception is that the way people make their purchase decisions has changed however Tractinsky and Lowengard (2007) stated that there exists a gap in empirical data regarding impact of e-commerce on consumer buying behaviour. This research therefore deems to fill this gap by analysing and evaluating the changes that have occurred in consumer buying behaviours due to e-commerce by taking the supermarket industry of UK as subject area.
1.2. Research Question
The main question for this research is to analyse “what impact E-Commerce has on the overall consumer buying behaviour” with sub-questions as follows:
- What are the different types of consumer buying behaviours
- How behaviours impact on the way consumers make purchase decisions
- Has E-Commerce changed the way consumers make their purchase decisions
1.3. Research Objectives
The following research objectives are defined for this research:
- To identify and evaluate different consumer buying behaviours
- To investigate the impact of E-Commerce on consumer behaviours
- To suggest improvements in e-commerce for future development
1.6. Significance of Research
International World Stats (2009) stated that there are more than 1.5 billion users worldwide that use web thus contributing trade and globalisation. Researchers such as Rha et al. (2002) and Urban (2003) stated that this increase in the global users also allows consumer empowerment and sophistication.
The increase in online purchases has been reported by Nielsen (2008) report which showed South Korea’s 99% internet users making online purchases followed by other countries such as Germany, UK, and Japan. Companies have started integrating e-business strategies in their business models and every organisation, irrespective of the industry or sector they belong to, develops their e-commerce enabled official website. This, according to Panagaria (2007), not only allows them to increase their sales but also facilitates their customers for making their purchases.
Over the past two decades, a lot of research has been conducted on the impact of e-Business and e-Commerce on the overall organisational performance such as on brand development (Bianchini and Parente, 2010), Intellectual Property Rights (Rao et al., 2008), team development (Montoya et al., 2009), natural environment (Catulli and Fryer, 2012), and employee rights and development (Townsend and Bennett, 2003; Panagaria, 2007; Morantz, 2014).
However little has been done on the way consumer buying behaviours have changed. This means that there is a gap present in empirical research on the way behaviours of consumers have changed due to the integration of e-commerce in business models of organisations. This research will therefore fill this gap in the literature and will provide a base for future research in this aspect of E-Commerce.
1.7. Structure of this study
This first chapter provides basic information about the research, introduces the topic, provides research question, and defines research objectives. Furthermore, the chapter also introduces why this research is significant. This chapter also provides a brief about how this study is structured in order to make it easier for readers.
The second chapter conducts extensive critical review of pre-published literature regarding different elements discussed in this study. The chapter uses many secondary sources such as articles, books, newspapers, and other materials to develop relevant knowledge required for this study.
The third chapter provides the methodology used by the study in completion. The chapter provides the inherent philosophy of this research, the research approach adapted, the sources used, and the data instruments utilised. The chapter also provides ethical and moral considerations while conducting this research and the way it was confirmed that the research is valid and reliable.
The fifth chapter presents the collected data and then uses the accumulated data to conduct different analysis in order to generate findings. Different statistical tests are provided in the chapter that were conducted using SPSS, a computer based statistical software. The presentation is in the shape of charts, graphs, and tables.
The fifth chapter provides conclusive remarks on the basis of findings generated in the fourth chapter. The conclusions are distributed based on different objectives that the research was supposed to achieve. Furthermore, the chapter also provides recommendations for improvements in the e-commerce systems in order to ensure that further support and facilitation is provided to the users.
CHAPTER – 2: Literature Review
2.1. Defining E-Commerce
As the e-commerce definitions given by various sources differ significantly, it is important to adopt a clear and consistent definition of e-commerce.
- From a communication perspective, e-commerce is the delivery of goods, services, information, or payments over computer networks or other electronic means.
- From a service perspective, e-commerce is a tool that addresses the desire of firms, consumers, and management to cut service costs while improving the quality of goods and increasing the speed of service delivery.
- From an online perspective, e-commerce provides capability of buying and selling products and information on the Internet and other online service.
2.2. Internet as an Important Communication Tool
For long time, consumers and marketer have had few sources of getting and disseminating information regarding products or services. The traditional resources of information such as television, radio, newspapers, guide books and word of mouth were the only sources of getting information and were offered limited insight. These resources are not only expensive (publishing and distribution) but also provide limited space besides limited experience. Due to these budgetary and space constraints, information about small business were not only extremely difficult to post but also to access.
However, with the advent of internet, publishing and distribution of information became accessible and cheaper. Internet has improved the flow and quality of information by helping companies understand their customers better through free information sharing in real time. It has connected companies and customers in such a way that both parties are able to better communicate with each other through company websites (online review), blogs, social media etc. Therefore, companies can offer products and services according to customer needs (Varadajan and Yadav, 200l).
The internet has also brought many challenges for companies. Consumer pressure on companies has increased because customers pass on information to other online users about company products and services by online customer reviews, blogs or social media (Chaffey et al, 2009). Online communication tools like company website (where company encourage customers to provide their reviews), online forums and social media encourage customers to share their experience which not only spreads product or service information through word of mouth but also enables a company to understand exactly what customers want.
With increase in Internet users (Table 2.1), company and customers relationship has transformed and communication has become transparent. Now online consumers no longer play a passive role but freely give their views about the products and services which could win a negative reputation for the company should the company fail to meet customer demands (Chaffey et al, 2009).
| Geography | Internet users |
| World Wide | 1.97 billion |
| Asia | 825.1 million |
| Europe | 475 million |
| North America | 266 million |
| Latin America & Caribbean | 204 million |
| Africa | 110 million |
| Middle east | 63 million |
| Asia Pacific | 21 million |
Table 2.1: Internet usage based on different regions
(Source: Nacho Carnes, 2011)
Another study conducted by Leboff (2011) suggests that in online environment, consumers’ role is no more passive but actively engaged in communication which has brought many benefits and challenges. Now company messages spread quickly but there is a risk of negative reputation if company fails to satisfy the customer needs. This includes the quality of product, customer service provision, information available, packaging and parcelling options, and the ease of making payments. There is a need for companies to be cautious and considerate when using internet as a communication tool.
The ordinary people are considerably influenced by internet technology that witnesses a large numbers of websites registrations every year, for example registration of approximately 21.4 million websites by end of December 2010 (Kotler and Armsrong, 2001, p.23). Internet users grew massively every year as compared to other communication technologies, and stand around 2 billion worldwide (Nacho Carnes, 2011). According to statistics of NachoCarnes (2011), the following is the demographic information about internet user.
According to Internet World Statistics (2009), 49 million, almost 79% people have internet usage, and approximately 70% house hold have internet access (see figure 2.5). Where highest access recorded is in London area (80%) according to Office of National Statistic (2009). An increase in number of internet users had been recorded by Office of National statistic by the year 2009, where total of 63 percent of households had internet access (56 % in 2008), where 90% of whom had broadband connections.
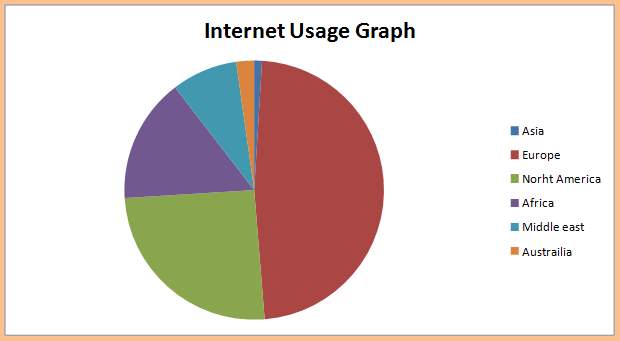
Figure 2.5: Demographic Representation
(Source: Based on Nacho Carnes, 2011)
2.3. E-Commerce Background
International World Stats (2009) stated that there are more than 1.5 billion users worldwide thus contributing trade and globalisation. Researchers such as Rha et al. (2002) and Urban (2003) stated that this increase in the global users allows consumer empowerment and sophistication. The increase in online purchases has been reported by Nielsen (2008) report which showed South Korea’s 99% internet users making online purchases followed by other countries such as Germany, UK, and Japan. Companies have started integrating e-business strategies in their business models and every organisation, irrespective of the industry or sector they belong to. This, according to Panagaria (2007), not only allows them to increase their sales but also facilitates their customers in making their purchases.
Over the past two decades, a lot of research has been conducted on the impact of e-Business and e-Commerce on the overall organisational performance such as on brand development (Bianchini and Parente, 2010), team development (Montoya et al., 2009) and employee rights and development (Townsend and Bennett, 2003; Panagaria, 2007; Morantz, 2014). However little has been done on the way consumer buying behaviours have changed. Therefore, there is a gap present in empirical research on the way behaviours of consumers have changed due to the integration of e-commerce in business models of organisations.
A study conducted by Hjort et al. (2013) on consumer segmentation based on buying and returning behaviour stated that although a vast amount of data is collected through e-commerce, it is seldom used to identify the change in consumer behaviours over the period of time. Their study was two-fold as it tested empirically whether strategies that are based on “one size fits all” fits their selected industry, and secondly it analysed whether returning consumers create profitability. The transactional sales and return data that was used could have also been used to identify the change in buying behaviours, selection of products or change in them, and the variety of choices that impact the decision making process.
However, Ericsson (2011) stated that buying behaviours of consumers using e-commerce cannot be homogeneous due to the reason that the consumer goods are fast-moving with a lot smaller lifecycle as compared to products couple of decades ago. Godsell et al. (2011) propagated that analysing the consumer behaviour could help organisations to differentiate their products and their supply chain strategies in order to match the changes. Gattorna (2010) is of the view that with the integration of e-commerce and the influence of social media, where consumers can share their views, has had a large impact on how people observe, gather information about different alternatives, select a certain product, and make a purchase decision.
Wen (2009) used travel industry to analyse the factors affecting the online travel buying decisions using factors such as quality of website design, customer trust, and customer satisfaction. The study found that e-commerce sites with better information quality, professional design, and authentic security of financial data gain better trust and confidence from consumers and increased chances of consumers making purchases.
2.3.1. Customer Perception and Attitude about E-Commerce
Exploring the relationship between consumer choices and income is vital in e-commerce. An important theory in this regard is known as the consumer theory (in economics) which analyses on balancing the relationship of consumers preferences to consumer budget for maximum product utilisation (Leboff, 2011). The theory emphases that consumers try to maximise their benefits for the amount of money they spend to purchase a product keeping in mind restriction imposed by budgetary constraints on their choices. The theory also looks into effects of consumer’s preferences, substitution, and income on the their buying decisions (Prenzel, 2010)
Behaviour can be affected by numerous cultural influences and environmental elements. Understanding the behaviour of the consumers is of vital importance for the success of the end products (Lee et al., 2008). In order to be successful in its e-commerce strategy, a company needs to know reasons behind consumers buying decisions. Since only few products appeal to all customers, an online strategy should focus on understanding the values of targeted customers through the use of focus groups, surveys and psychological analysis, on which organisations can plan their future strategy. (Park and Kim, 2008)
E-commerce provides an opportunity for businesses to effectively communicate to its existing and potential new customers. However businesses need to be well aware of customer perception regarding their products, since online customers are quite different as compared to traditional customers (Huang et al., 2009). The focus of an online customer is on information such as product price and its value for money, so to project product quality, one approach is to promote it through a website that has a design based on relevant, detailed and informative contents which appeal the customer.
E-commerce websites should effectively meet the customer needs (Nutley, 2011). Consumers compare their perceptions of product performance with set standards. There is confirmation of results when the perceived performance matches standards, whereas disconfirmation results from a mismatch. Confirmation and rejections determine consumer satisfaction or dissatisfaction (Varadarajan and Yadav, 2002).
However, consumer attitude is an important element when studying their shopping behaviour online. Sharma (2011) summarised nine factors to assess the consumer perception toward online shopping, He stated these factors to be risk perception, control, convenience, affordability, quality of service, and level of difficulty in using the websites. Several factors that can influence the customer’s online shopping behaviour are categorised into four major categories: value of product, online experience, quality of service and risk perceptions of internet retail shopping. Consumer trust is also influenced by retailer size and reputation (Nutley, 2011).
2.3.2. Consumer Attitude towards E-Commerce Tools
According to the American Customer Satisfaction Index (ACSI) second quarter report, customer satisfaction with e-commerce web sites has reached a new height after a dip in 2003. ACSI scores for e-business rose to an all-time high of 79.3 on the index’s 100-point scale (Changehien et al, 2004). Satisfaction with e-business sites, namely, portals, search engines, and information sites, surpassed the national ACSI aggregate score, but still lag behind consumer sites. The jump in year 2013 was driven largely by Google’s 10 percent climb to a score of 86, the highest customer satisfaction score ever recorded in the e-business report.
Consumer’s attitude towards online shopping is also crucial dynamic of e-commerce studies. A recent report by Saaksjarvi and Pol (2007) explains that customer acquisition by email marketing is gaining momentum for the last four years. These change in consumer attitudes, they stated, is based on many benefits that e-commerce provides such as:
- Easy access to information regarding products and services
- Quality of information on products and services
- Convenience for customers
- Expanding choices for customers
- Creating new markets
- Development of interactive relationships with customers
- Improved customer services
- Development of organisational image
- Saving time
- Customisation of products and services
- Reduction of operational cost
- Simplifying purchase process
- Active interaction with business partners
- Searching and founding new business partnerships.
2.4. The Emerging E-Marketing
Electronic marketing or e-marketing is essentially any marketing activity that is conducted online through the use of internet technologies. It comprises not only advertising that is shown on websites, but also other kinds of online activities like email and social networking (Gibson, 2011). Every aspect of e-marketing is digital, meaning that it is electronic information that is transmitted on a computer or similar device, though naturally it can tie in with traditional offline advertising and sales too.
E-marketing is different to that of traditional marketing and attracts active audience instead of passive audience, which are in full control of which information to browse and whose website they should visit (Gibson, 2011). So it takes considerable time and expenses to identify potential customer in e-marketing but provides equal opportunities to the marketers where they able to maximise their business exposure (Andreassen and Streukens, 2009).
2.4.1. E-Marketing Tools and Trends
In e-marketing it is extremely important to differentiate the product or services from the other competitors because internet readily provides means to compare different product online and show instant results. Organisations require skills for gathering and analyses of information extracted from online markets to make future strategies for organisations.
Websites are the first step in offering products and services to the consumer and providing them with details of what the product does through audio and visual clips. This is where the organisations deliver their view of their products and their belief of how the product or service will help consumers. Websites are among the most effective and useful techniques in the tools and methods of e-Marketing (Moe, 2003).
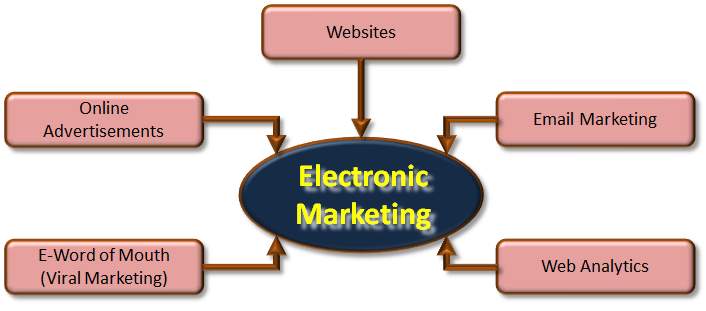
Figure 2.6: Electronic Marketing Trends and Mediums
(Source: Adopted from Gibson, 2011)
2.4.1.2. Employing Email Marketing Methods
E-Mail marketing method is same as sending Direct Mails in traditional marketing but without the hassle of designing, printing, and posting costs. The consumer content is gathered through their use of official websites and then related and relevant products and services are offered to them through sending e-mails of product details that can interest them. However, sending too many e-Mails are considered to be ‘spamming’ and is not appreciated by the customers.
2.4.1.3. Online Advertisements
Online Advertisement is another avenue that companies utilise in the shape of e-Marketing medium. The advertisements are placed on ‘partner’ websites where the browsing consumers can view the offered products and services. These offers are made based on the ‘clicks’ that the user has made while browsing the partner website. Moreover, advertisements are placed by search engines such as Google and Yahoo based on the search string that the user provided (Rust and Lemon, 2001).
Web Analytics means to study the user impact of a given website used by companies employing e-Commerce or websites to measure specific details such as the users visiting their sites, number of users that visited it, and the referee website through which they came. It is necessary if there is a partnership with other sites that are paid on the pay-per-click method where each customer coming from their website and making a successful purchase will generate money for the referring website (Park and Kim, 2008). Such information is necessary for organisations to understand which their consumers are interested in and are considered a strong force in e-Marketing strategies (Leboff, 2011).
2.4.1.5. Electronic Word of Mouth (Viral Marketing)
This form of marketing involves the exponential spread of a marketing message by online word of mouth (sometimes referred to a “word of mouse”). A major component of viral communication is the ‘meme’, a message that spreads virally and embeds itself in the collective. Viral marketing is closely tied to social media, since social media platforms and their sharing functionality are the main way that a message is able to “go viral” online (Cheung et al., 2008). Viral marketing does not make a holistic e-marketing campaign and should be just one of many tools used to create awareness and encourage interactions.
More than ever before, brands are creating personas and identities around themselves rather than the products they sell. The online space allows customers to interact and converse with the brand personally and directly.
2.4.1.7. Advertisement fatigue
Web users have become very familiar with online advertising and have learned to tune it out or have even installed programs like ‘AdBlock Plus’ to block it altogether. Marketers today have to think of very innovative and eye-catching strategies to entice wary viewers.
Virtually all online advertising is targeted to reach specific readers. With the immense amount of personal and usage data currently available, targeting can be done automatically and extremely successfully.
2.5. Critical Success Factors of E-Marketing Strategy
Any rushed or unstructured e-marketing attempt is doomed to failure and invisibility (Andreassen and Streukens, 2009). Simply creating a website or Facebook profile doesn’t mean that you are marketing yourself online; using these applications and tools are just steps in one small part of the on-going, intensive and risky process (Awad and Ragowsky, 2008). Planning involves aspects like growing your contact base, organising strategically timed promotions, scheduling time for social network maintenance and monitoring, ensuring consistency throughout all communications, spreading the information manually, and so on (Chevalier and Mayzlin, 2006). With a little thought and care and with the proper tools in place, you can get massive returns for relatively little money and time. It all depends on approach, determination and perseverance of the organisation (Doh and Hwang, 2009).
In order to assist strategists in the formulation of business strategies, models such as The Four Ps (product, price, placement and promotion) and the Porter Five Forces (Industry rivalry, bargaining power of buyers, buying power of suppliers, threat of new entrants, and threat of alternative products) analysis have become widely adopted (Doh and Hwang, 2009). Both of these tools assist in evaluating the kind of value the business is offering and the competitiveness of the market. The Internet, however, impacts hugely on both of these aspects (Forman et al., 2008), prompting us to re-examine and adapt traditional models to the changing market environment and new consumer behaviours.
The Four Ps approach is fundamentally changed by the Internet and needs to be looked at in view of the context offered by digitally connected media (Goldsmith, 2006). In addition to the existing Four Ps, the Internet prompts the consideration of a new P: People. This final element speaks to examining the powerful human element that the digitally connected world permits: personalisation, peer-to-peer sharing, communities and consumer-centric organisations which allow people to participate in the brand story (Hu et al., 2008).
The Porter Five Forces analysis is another business tool that needs to be adapted for an online perspective (Kumar and Benbasat, 2006). This model assists in determining the competitive intensity and therefore the attractiveness of a market (Lee and Lee, 2009). The Internet’s low barrier to entry has allowed the proliferation of businesses in the online space, as well as providing infinite choices for customers in terms of products and services, making it important to consider new factors when devising a marketing strategy. Strategy is an imperative first step in establishing the positioning of your brand within the market and providing a roadmap in order for you to achieve your end goals (Kumar and Benbasat, 2006). There may be many different paths to reach these goals, but an effective strategy weighs the available options and makes a choice, based on the internal and external brand situation.
According to Dan Bosomworth and Dr Dave Chaffey a successful e-marketing strategy should be based on the context (organisational or stakeholders), how to achieve organisational objectives, use value exchange to analyse the objectives, selection of best affordable and suitable marketing techniques for evaluation of marketing goals, use of metrics to measure key performance indicators and optimisation for a continuous refining of e-marketing strategy (Bosomworth and Chaffey, 2013).
E-marketing has technology at its heart and understanding the value that technology can add to people experiences of brand. The variety of new tools and tactics offered by the digital medium should inform strategic choices. E-marketing strategy is highly empirical and strategic thinking should start by being mindful of Return of Investment (ROI) and the ways in which this can be measured. This measurement-focused thinking will allow companies to optimise their tactics and performance in order to create the most valuable, brand, the most optimised conversion funnels and the highest ROI.3270
Chapter 3: Methodology
Research Methodology
Research methodology is an aspect which is related to the perspective and preferences of the how the researcher approaches to conduct the research. It often includes the study and selection of philosophies, designs, different approaches and styles that are applicable. According to Kumar and Phrommathed, (2009) the initial step to carry out research is by developing a structure of how to attain knowledge, this can be done by researching about the previous research in order to find out how far the people have been on the selected research.
Research Method
The research methods comprises of two main methods i.e. qualitative and quantitative. The former is focused on the quality and characteristics of the research while the latter is more lenient towards the empirical aspect of the research (Kothari, 2004). The research method that is chosen is always based upon the rationale of the topic and the perspective and preferences of the researcher. Furthermore, there is another method called mixed method that includes both the qualitative and quantitative method for the collection of data and focuses on both the economical and empirical aspects as well as theoretical evidence and scholarly views (Welman et al., 2005).
Applied Method
According to the nature of the topic the research method that is fairly applicable is the mixed method. This method would enable the researcher to deeply understand the research requirements and fulfil the criteria of the research. To analyze the consumer behaviour and impacts of E-commerce it is essential gather data with the help of applying mixed method to conduct the research.
The qualitative data would be collected by the help of various sources including the views of the industrialists and business tycoons that are altering the marketing ways which affects the consumer behaviour. Also, the academic journals, scholarly views, case studies and newspapers would be utilized to extract the required data. In order to conduct the quantitative data, the questionnaires would be prepared for the customers and different business chains which would help in analyzing and interpreting the research questions accordingly.
Research Approach
The research approach is selected in accordance to the research philosophy that is applied to conduct and analyze data (Patton, 2005). The research approach and philosophies collectively enables the researcher to be acknowledged about the requirements of the research and the methods to accumulate and validate the collected data (Marcyzk et al., 2005). The two main research approached that are mainly applied in various research topics are induction and deduction according to the prerequisites and necessities of the researchers.
Applied Approach
As the induction is based upon the perspectives of the individuals and the observations whereas deduction is primarily focused upon the quantitative methods of collecting and analyzing data which enables the researcher to implement both the inductive and deductive approaches. The nature of the topic require both quantitative and qualitative analysis thus it would also allow the researcher to develop outcomes accordingly. Questionnaires were formulated according to the requirements of the research to carry out the research.
Research Design
In order to complete the research process certain tools and tactics are required which are provided by the research design. By the help of research design the research questions can be answered with accuracy and precision. The choice of research design is dependent upon the requirements upon the research and perspective of the rationale of the topic (Creswell, 2017). Research designs are either primary research based or secondary research and in some cased both the researches are used to support the gathered information.
Applied Design
In accordance with the research topic and criteria the design selected for the research is descriptive design which comprises of both the exploratory and explanatory research designs. Exploratory research is centered towards the exploring which mainly comprises the primary data collection activities and no secondary evidence is used in this research while in the explanatory research the situation is entirely opposite and the research that is conducted in this design is mainly by the aid of secondary sources i.e. the researcher uses the existing techniques to form hypothesis and accumulate relative theories.
Research Philosophy
Research philosophy is considered as an essential element to be focused upon while conducting research because it aids the researcher in collecting and analyze the research in a proper way (Crossan, 2003). The research philosophy is selected according to the topic of interest. The philosophies that are most practiced includes interpretivism and positivism but in some cases the research philosophies realism and pragmatism are also applied. Each philosophy tends to answer the research questions in an entirely different manner which can alter the outcomes but the philosophy must always be chosen that a way which fulfils all the requirements of the research (Edson et al., 2016).
Applied Philosophy
The applied philosophy is realism as the growth of e-commerce is rising every single day and consumer buying behaviors changes as the new and updated methods of shopping are being introduced. The realism philosophy would allow the researcher to interpret knowledge thoroughly by both interpretive and positivism approaches.
Validity of Data
The fundamental aspect of the research is to validate the data and provide evidence that the data that is collected is accurate (Guion, 2002). If the data is authentic and precise then the conclusion can be drawn more certainly. To validate the secondary data, the data is gathered from the famous scholar’s journals, books and articles and the primary data is purely based upon the experiences and questionnaire deductions made by the individual. The scholars and academics are referenced and credited in order to show that the data is authentic and validated. In quantitative research, the use of reliability is common but now with the passage of time it is required in the qualitative research as well, to show that the data that is used is validated and accurate. In the research paradigm, data is highly essential to be validated or there would be no use of the research (Golafshani, 2003).
Sampling
Sampling is an essential part of the research which shows the quality of the results and findings that are concluded in the research process. The process of sampling includes the gathering of required data on the topic of interest by the group of people by whom proper knowledge can be generated (Cochran, 2007). In this specific research the group of those individuals who are active in both physical and online shopping are gathered so that they can be interviewed so that the researcher can fulfil the requirements of the research.
Sampling helps in extracting the desired information from the desired population. Random sampling helps in generalizing which is highly important for the researcher. It gives idea and new perspective to the researcher which then fulfils the demand of the research. The kind of sampling that is done in this research is the stratified sampling which enables the researcher to select specific people from different categories from a population. It is mostly used to characterize the population which can’t be done randomly. This is also done to compare two different populations to prove a point.
Chapter 4: Context
This study shows the influencing power of E-commerce on the buying behaviour and pattern of customers and how it has changed and advanced. Over the last two decades the E-commerce had advanced such a way that it spread into almost the whole world. The rise of E-commerce was seen as a great opportunity to enhance business and adapted by most of the businesses. This adaptation brought revolution in the consumer buying behavior and it has been observed that most of the people switched to online shopping and the businesses have altered their strategies to advance their marketing ways in order to increase their sales in this category. Mostly all the electronic systems were made for one purpose i.e. to save time and be efficient (Turban et al., 2002).
The main aim of businesses in adapting E-commerce is to provide ease to people so that they won’t have to go any physical stores and everything comes in handy and they govern most of their purchases by their fingertips. Most of the famous industries and firms are now made themselves available on the Internet as they have observed the demands of the consumers. Only physical stores are not enough or the businesses now, their online presence is equally valuable which also includes their official websites and the services that they are capable of providing. Furthermore, E-commerce is tool by which the firms have the capability to save time and increase their profit margin and by simplifying the purchase process a business can rise as more advanced and revolutionized.
E-commerce has not only changed the purchasing pattern of the customers but also their perception, perspective and attitudes in shopping. Even in the area of health and digital technology. It is now an essential component which demands a lot of focus by the businesses and to blend in and be prominent and dominant in the social environment. Also, in the supply chain of company and electronic data interchange it plays a significant role. This study shows how e-commerce strengthens the communities and influences their standpoints by introducing promotions, marketing methods, created value and reliability. In this study, by attaining the outlooks of individuals, the extent of effect of E-commerce would be identified upon consumers, stakeholders and businesses. Delone and Mclean (2004) states that, the businesses invests so much in E-commerce so it is necessary that the impact on consumers would be at large. Grandon (2004) discusses the impact of E-commerce by stating that it is a combination of business and electronic which aims at success and requires additional management.
Chapter 5: Presentation & Discussion
Presentation of Data
Tables and charts. (To be done)
- Age range older generation in store and 40% for 18-34
- Income Range
- Online consumers, click and collect and in store
- Behavioural buying types
- Users of ecommerce
- Factors that influence ecommerce decision
- Market share of major supermarkets (5 major)
Correlation between income range and online shoppers.
Access to internet.
Discussion
- Types of consumer buying behaviour
4 different types:
- Complex buying behaviour
- Variety seeking behaviour
- Dissonance buying behaviour
- Habitual buying behaviour
- What factors affected consumer behaviour changes? Brand loyalty PWc Report 2017/ Convenience over cost
- Why prefer ecommerce or abstain from it? Factors
- Link to business and operations. How e commerce ties into strategy. Example Morrison’s and ocado.
- Behaviours before and after ecommerce introduction by supermarkets. Rolls outs explored. Click and collect options.
- Impact of ecommerce on purchase decisions..bulk buying for offers. Accessibility and access to offers.
Appendices
Appendix – 1: Questionnaire
– Thank you for your co-operation –
Please complete the following questions based on the E Commerce grocery shopping project. Thank you for your time.
E Commerce Survey
- For classification purposes, what gender do you identify with?
Male
Female
Other. Please State: ……………………………………………
- What is your household’s gross annual income for the past year?
£10 000-£20 000
£20 000- £30 000
£30 000- £40 000
£40 000-£ 50 000
£50 000 and Above
- Are you jointly or solely responsible for the grocery shopping in your household?
Solely Responsible
Jointly Responsible
- Do you use e commerce (online shopping) in your grocery shopping?
Yes
No
- If no to question 4, would you be willing try the service in the next 12 months?
Yes
No
- Which E commerce option have you heard of before?
Virtual Supermarket
Click and Collect In Store
Home Delivery
- Which E Commerce grocery option have you tried or be willing to try in the next 12 months?
Virtual Supermarket
Click and Collect In Store
Home Delivery
- What factors have played a part in your decision to use or abstain from E Commerce in your monthly grocery shop?
Special Offers
Convenience of Bulk Shop Delivery
Lack of Inspection of Perishables
Other (Please State) ……………………………………………………………….
- Has the introduction of online grocery shopping affected your grocery shopping habits?
Yes
No
- If yes to question 9, how has it?
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- What disadvantages have you experienced with e commerce grocery shopping?
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Do you see yourself and your household relying more or less on e commerce for your grocery shopping in the next 12 months?
A loss less
About the same
A lot more
- What recommendations would you suggest for the current ecommerce grocery shopping process?
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Thank you for your time
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
All TagsContent relating to: "Consumer Decisions"
The consumer decision making process involves how consumers identify their needs and gather and process information prior to a purchase. Consumer decisions involve how the emotions and preferences of consumers can impact their buying decisions.
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this dissertation and no longer wish to have your work published on the UKDiss.com website then please:




